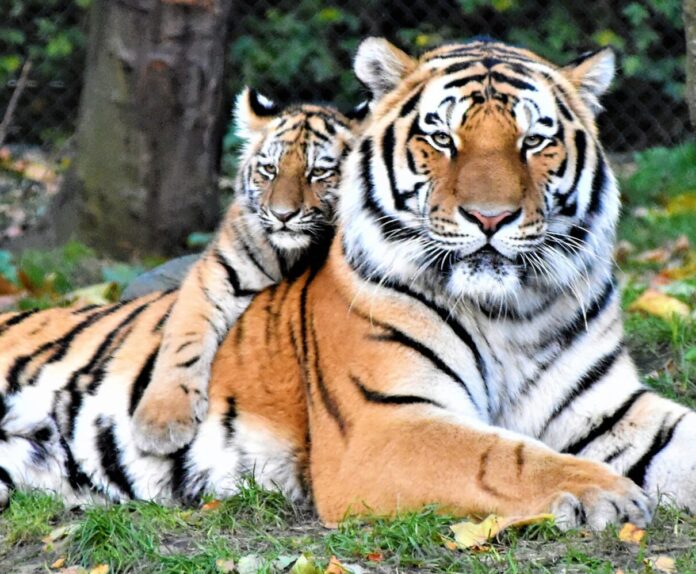
Tigers, the largest of all big cats, command awe and admiration with their powerful presence, striking beauty, and elusive nature. Beyond their majestic appearance, these magnificent predators possess fascinating traits and behaviors that make them truly remarkable creatures. Here are three things you may not know about tigers.
Diverse Habitats
While commonly associated with dense jungles and lush forests, tigers are highly adaptable creatures capable of thriving in a variety of habitats, including grasslands, mangrove swamps, and even snowy mountain ranges. Tigers are found across a wide geographic range spanning Asia, from the tropical forests of India and Indonesia to the taiga forests of Russia and the snow-covered landscapes of Siberia. Their ability to inhabit such diverse environments is a testament to their remarkable adaptability and ecological flexibility, allowing them to persist in a changing world despite habitat loss and human encroachment.
@kaitlinthekeeper Tigers can be such divas 💁🏻♀️ #harvest #tiger #absolutelynot #cute #animals ♬ original sound – Kaitlin Richard
Complex Social Structures
Despite their solitary reputation, tigers exhibit complex social behaviors and hierarchical structures, particularly in areas with abundant prey and overlapping territories. Female tigers are generally more social than males, often forming loose associations with other females and their offspring. Male tigers, on the other hand, are typically solitary, establishing and defending large territories to maximize access to mates and resources. However, interactions between tigers can vary widely depending on factors such as population density, prey availability, and environmental conditions, highlighting the dynamic nature of tiger social dynamics.
@jajahayequiz #Tiger #Petting ♬ sonido original – jajahayequiz
Role In Ecosystem Health
As apex predators, tigers play a crucial role in maintaining the health and balance of their ecosystems. By regulating prey populations and shaping habitat structure through their hunting behavior, tigers help maintain biodiversity and ecosystem resilience. Their presence also has cascading effects on other species, influencing the behavior and distribution of prey species and shaping the structure of plant communities. Moreover, tigers serve as indicators of ecosystem health, with their presence or absence serving as a barometer of the overall well-being of their habitats.